The Art of Blog Writing: Crafting Engaging and Informative Articles
Blog writing is a powerful tool for businesses and individuals alike to share their thoughts, insights, and expertise with the world. Whether you’re looking to attract new customers, establish yourself as an authority in your field, or simply express your creativity, writing compelling blog articles can make a significant impact.
Here are some key tips to help you craft engaging and informative blog posts:
- Know Your Audience: Before you start writing, take the time to understand who your target audience is. Tailor your content to their interests, needs, and preferences to ensure maximum engagement.
- Create Catchy Headlines: The headline is the first thing readers see. Make it attention-grabbing and relevant to entice them to click and read more.
- Provide Value: Offer valuable information, insights, or entertainment in your blog posts. This will keep readers coming back for more and establish you as a trusted source of content.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate images, infographics, videos, or other visual elements to break up text and make your posts more visually appealing.
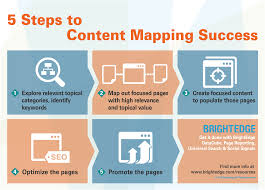
- Optimize for SEO: Use relevant keywords, meta descriptions, and alt tags to improve your blog’s visibility in search engine results.
- Engage with Your Audience: Encourage comments, feedback, and social sharing to foster a sense of community around your blog.
Blogging is not just about writing; it’s about connecting with your audience on a deeper level. By following these tips and putting your unique voice into each post, you can create blog articles that resonate with readers and leave a lasting impression.
If you’re ready to start crafting compelling blog content that drives engagement and boosts your online presence, get in touch with us at iPower.eu. Our team of experienced writers can help bring your ideas to life through captivating blog articles that captivate audiences and drive results.
Elevate your online presence: Write captivating blog articles with us!